Seize the moment when the sun appears! Study: 10 minutes of sunbathing can provide "8 health benefits"
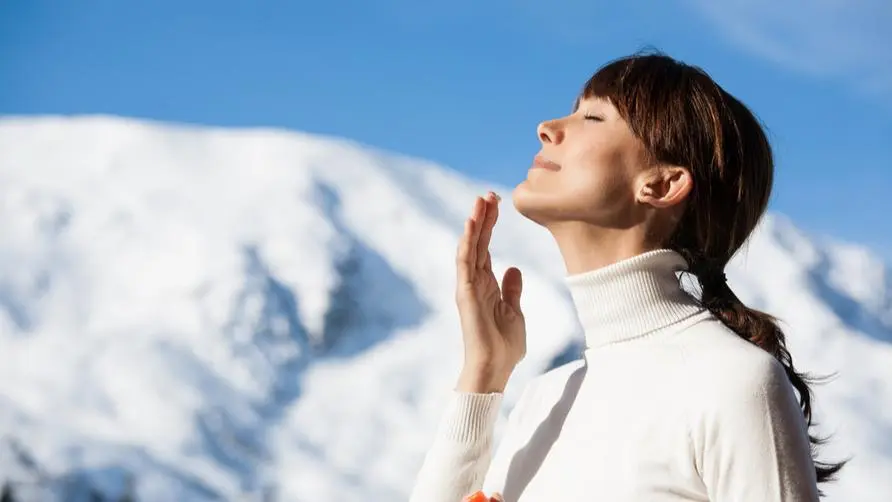

It has been raining for days and the cold wave is raging. Do you feel that your whole body is “about to get moldy”? You might as well take advantage of the opportunity this week for the sun to show its face and get more exposure to the sun. In addition to keeping the body warm, sunbathing can also have 8 positive benefits to the body according to many studies: moderate exposure to the sun:
1. Improve sleep quality
According to the Health Management Center of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the human body secretes “melatonin” before going to bed to help fall asleep. Getting up one hour earlier in the morning to expose yourself to natural light can help reduce melatonin levels and make you more energetic in the morning. In addition, exposure to sunlight can also adjust the body’s circadian rhythm, secrete melatonin normally before going to bed, and help you fall asleep.
2. Increase daytime energy
As mentioned before, exposure to sunlight helps the body reduce the secretion of melatonin, which helps the body wake up from drowsiness faster. The National Institute of Health (NIH) also pointed out that for travelers, shift workers, or people who often need to reverse day and night, “sleeping” is not a way to adjust the biological clock, but to expose enough sunlight, especially if you can be exposed to 1 hour of natural light in the morning. Can help you sleep at night.
3. Reduce psychological stress
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), melatonin can reduce the body’s response to stress. For example, participating in outdoor activities can help the body regulate melatonin, thereby reducing stress levels. In addition, the American Psychological Association also recommends that patients suffering from “seasonal depression” (or those with related medical history) should have moderate exposure to natural light sources. The mood-relieving effect is no less effective than bright light therapy.
4. Strengthen bone tissue
Guidelines published by the U.S. National Institutes of Health indicate that the best and easiest source of vitamin D is “outdoor activities.” When exposed to sunlight, the body produces vitamin D on its own. Vitamin D is also a key nutrient that helps the body retain calcium and prevent bones from becoming brittle, thin, or misshapen.
5. Kill the source of allergies
In rainy or humid environments, mold may easily grow indoors, or excessive dust may accumulate due to environmental pollution, causing asthma or allergies. A study published in “BMC” found that sunlight can kill bacteria in dust; in the space where the subjects were located, about 12% of the bacteria survived in the room, but only 6% of the bacteria survived after exposure to ultraviolet light. It is recommended that people open curtains or windows in sunny weather to improve indoor air quality.
6. Strengthen the immune system
Guidelines published by the U.S. National Institutes of Health indicate that vitamin D is essential for maintaining the immune system, and exposure to sunlight can help strengthen the body’s immunity. A healthy immune system can help reduce the risk of illness, infection, and death after certain surgeries.
7. Extended life expectancy
The “Journal of Internal Medicine” study analyzed the results of 30,000 Swedish women, showing that subjects who were frequently exposed to the sun lived an average of about 6 months to 2 years longer than those who were less exposed to the sun, and also participated in more outdoor activities. or exercise. But is sun exposure causally associated with increased life expectancy? More research is needed to clarify.
8. Prevention of specific diseases
An analysis of nearly one million people by the British Medical Journal (BMJ) pointed out that vitamin D deficiency may be related to increased mortality from heart disease and cancer, and that vitamin D obtained from sun exposure is less effective than taking nutritional supplements. It’s more important. Another study published in the British Medical Journal also found that adequate amounts of vitamin D may be related to the prevention of breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Based on the above, although there are many benefits of sun exposure, too long exposure time is still too much. The Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare, Health Promotion Administration recommends that people avoid direct sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. and do sunscreen 2-3 times a week without applying sunscreen products and using moderate ventilation. Sunbathe for about 10-20 minutes each time to obtain sufficient amounts of vitamin D.
The Taiwan Health Promotion Administration also reminds people with darker skin tones that they can extend the sun exposure time appropriately, but exposure should not exceed 30 minutes at a time to avoid sunburn, skin peeling and other conditions. If your skin develops allergies, redness, swelling and itching after being exposed to the sun, you must consult a dermatologist immediately for further treatment.
Source:
“Four Myths” About Vitamin D Supplementation for Pregnant Mothers
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) - APA
Trusted Health Information from the National Institutes of Health
Daylight exposure modulates bacterial communities associated with household dust
Further reading: