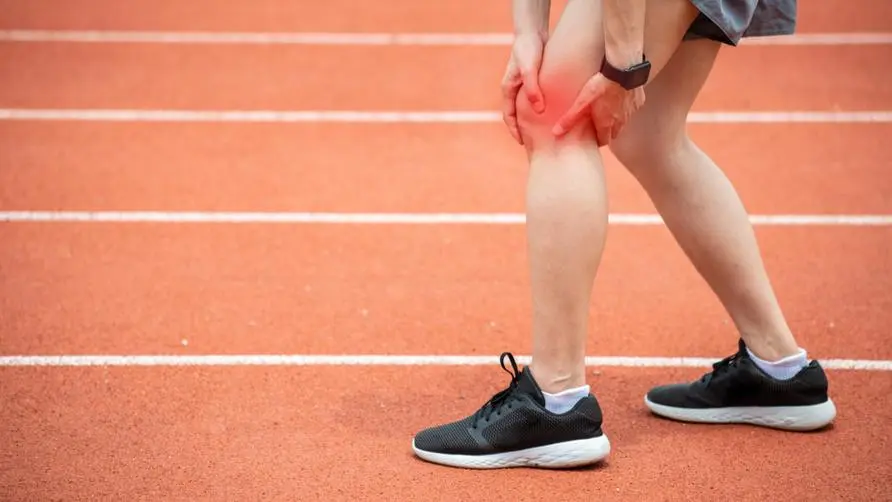
Is knee pain "runner's knee"? The causes of knee pain are very different. Exercise is more likely to cause patellar tendonitis.
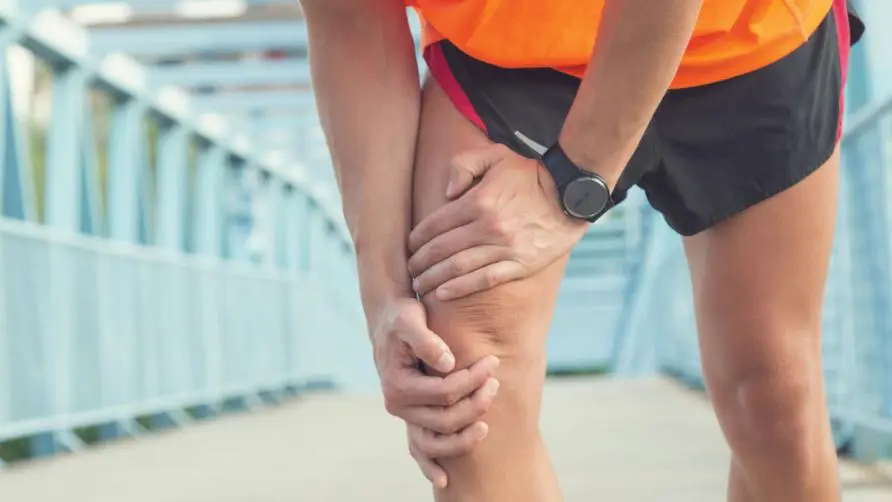

Is “runner’s knee” more than just one disease? What are the causes of knee pain?
Knee pain is the most common symptom of sports injuries caused by running. However, the pain occurs in the front, outside and inside of the knee, and the causes of the disease are also different. Dr. Wu Yicheng, the attending physician of the Sports Medicine Department of Lianxin International Hospital, said in an exclusive interview with “Biomedical Times” that pain occurring on the front side of the knee is more likely to be “patellar tendinitis” or “patellofemoral syndrome”; pain occurring on the outside is more likely to be related to “patellofemoral syndrome” “iliotibial band syndrome”. For people with flat or collapsed arches, they are prone to wear and tear on the inner side of the knee, which may lead to medial ligament strain or “anterior tendonitis”.
Jogging is becoming more and more popular in Taiwan, and many people suffer from “runner’s knee” pain. Dr. Wu Yicheng explained that “runner’s knee” is commonly known as “runner’s knee”. It is usually caused by cumulative wear and tear of running training to a certain extent, causing structural damage, or sports injuries caused by increased pressure on parts due to muscle imbalance, including the iliotibial band. Syndrome, patellofemoral syndrome, or patellofemoral tendinitis are all conditions of runner’s knee.
What is the difference between “iliotibial band syndrome” and “patellofemoral syndrome”?
Dr. Wu Yicheng said that iliotibial band syndrome, the most common runner’s knee problem, has different manifestations from patellofemoral syndrome. Iliotibial band syndrome is when pressure extends from the outside of the thigh to the tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus muscles to the outside of the knee. , sometimes also extending to the outside of the hip joint above the femur. As for patellofemoral syndrome, also known as patellar osteomalacia, it is mainly caused by poor sliding track of the patella, which leads to imbalance of muscles or base force around the patella and causes wear and tear. The pain is most common on the front of the knee.
However, running is not the only cause of runner’s knee." Dr. Wu Yicheng pointed out that various sports injuries covered by runner’s knee may not only occur in joggers. For example, “patellar tendonitis” also often occurs in “jumping” sports such as basketball and volleyball. Repeated actions of taking off and landing will cause changes in muscle strength and increase the pressure on the knee. It is easy to accumulate chronic microscopic inflammation in the patellar tendon. The injury eventually develops into patellar tendonitis. In addition, people who often engage in high-intensity mountain climbing and walking but lack muscle strength may overburden the knee tendons, which may lead to patellar tendonitis.
How is runner’s knee diagnosed? If the pain does not subside within 1-2 weeks, seek medical advice immediately.
When knee and surrounding pain occurs, how to diagnose the cause of sports injuries? Dr. Wu Yicheng explained that during the outpatient clinic, the location of the pain will be checked first, and then relevant physical examinations will be arranged. The patient will also be asked to perform basic exercises or squat to test the range of motion, and resistance testing may also be used to confirm the condition of muscles and tendons.
In terms of imaging examinations, X-rays have poor diagnostic capabilities in runner’s knee-related sports injuries and are mostly used to rule out injuries such as fractures or patellar valgus. When assessing possible causes related to runner’s knee, ultrasound is preferred to check for soft tissue injuries such as ligament damage and tendon damage. For example, patellar tendonitis will appear swollen or partially broken under ultrasound, and a preliminary differential diagnosis can be made. If deep structural damage such as the meniscus or anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments is suspected, further MRI co-diagnostic examinations need to be arranged.
Dr. Wu Yicheng reminds that the severity of sports injuries varies from person to person. If the symptoms gradually relieve after a few days to 1-2 weeks of rest, the symptoms can be assessed as mild; if the symptoms last for more than 1-2 weeks and the pain and discomfort gradually worsen. , you should consider medical examination. In particular, some patients continue to perform high-intensity training even after pain, which may lead to poor body repair ability. It is recommended to seek evaluation from professional coaches and sports medicine specialists to avoid continued accumulation of damage and leading to more serious sports injuries.
Further reading: The “recovery cost” of injured knee joints is the top 5 sports that reveal the highest knee injuries: the first place is not basketball