Can't tell if food is contaminated with "bongkrekic acid"? Experts reveal the fatal dose: reheating and cooking are useless

Can bongkrekic acid cause severe food poisoning? Be careful when storing these foods for too long!
A suspected mass food poisoning incident broke out at the Malaysian vegetarian restaurant “Baolin Tea Room” in Taipei’s Xinyi District; the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare held a press conference yesterday (28th) to announce the preliminary investigation results. The prosecutors tested the remains of the two deceased and indeed found " “bongkrekic acid” toxin, consistent with the opinions of the expert meeting, is also the first bongkrekic acid poisoning incident in Taiwan.
What exactly is bongkrekic acid? According to research published by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), bongkrekic acid is a “mitochondrial toxin” rather than a bacterium. It mainly inhibits the “adenine nucleotide transporter” (ANT, which functions to transport adenine nucleotides into Transported from the cytoplasm to the interior of the mitochondria, thereby participating in the energy metabolism process of the mitochondria), rather than the electron transport chain, causing human poisoning.
Is 1 mg a dose potentially life-threatening? The 6 most troublesome properties of bongkrekic acid
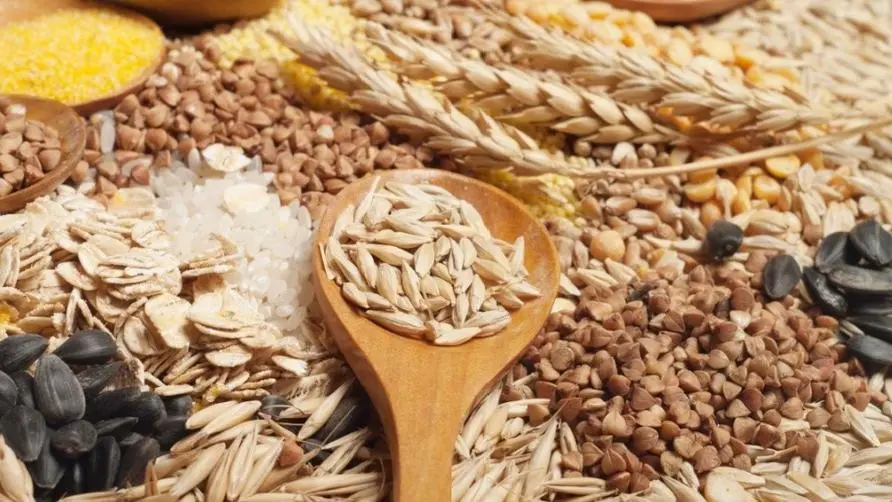
Bongkrekic acid has been linked to severe foodborne disease outbreaks and is commonly found in fermented rice products, fermented corn products, fermented coconut products, fermented potato products, or foods such as white fungus and fungus that have been soaked for too long. Most of the food contaminated by bongkrekic acid will not become smelly or moldy like other spoiled food; on the contrary, its appearance, smell and taste may be the same as before the contamination, which is often difficult for humans to detect before eating.
Research points out that the reproduction of bongkrekic acid roughly depends on two major conditions: temperature and fatty acids. bongkrekic acid is easy to grow in a warm environment (22-30 degrees Celsius) with a neutral pH value; in addition, fermented coconut, corn and other foods contain high concentrations of fatty acids (Fatty Acid), which are also considered to promote the reproduction of bongkrekic acid one of the reasons. Taking fermented coconut products as an example, lauric acid, myristic acid and palmitic acid account for 71.5-74.5% of the fatty acids in coconut oil.
There are currently different opinions on the lethal dose of bongkrekic acid. The “Food Toxicology Manual” once stated that a dose of 1-1.5 mg may be fatal to humans; other animal studies pointed out that oral administration of a dose of 2 mg of bongkrekic acid will cause mice to die in 2 -Death within 5 hours. The Australian Institute of Food Science and Technology used coconut products as a culture dish for bongkrekic acid. The results showed that the toxin production could reach 2-4 mg on the second day of culture.
Is it possible to be poisoned within a day if you accidentally consume bongkrekic acid? If you experience “14 major symptoms”, you should seek medical treatment as soon as possible
What are the possible signs if you accidentally eat food contaminated with bongkrekic acid? Epidemiological analysis published in “PLOS ONE” shows that poisoned persons may suffer from epigastric discomfort, nausea, vomiting, mild diarrhea, dizziness, weakness, severe jaundice, liver enlargement, subcutaneous bleeding, vomiting blood, hematuria, and low urine output. , confusion, restlessness, convulsions, shock, generally speaking, there are few symptoms of fever.
The analysis pointed out that bongkrekic acid outbreaks usually occur in warm summers. Due to its extremely heat-resistant characteristics, even if the contaminated food is re-cooked, its toxicity cannot be destroyed; in addition, bongkrekic acid is to be detected through human secretions such as feces. The possibility is extremely low and very unreliable. Even if genetic sequencing is used for identification, it may lead to erroneous test results.
How to avoid food poisoning caused by bongkrekic acid? Experts call for: 6 things to do every day!
Currently, there are no treatment guidelines for patients with bongkrekic acid poisoning, which means there is no specific drug that is effective and can detoxify the poison. According to the National Capital Poison Center (NCPC), a non-profit organization in the United States, the mortality rate is 40-100%; death from multiple organ failure may occur within one day of the first signs and symptoms. The Singapore Food Agency (SFA) also appeals to the public that if they want to stay away from the threat of bongkrekic acid, they must observe the following before eating:
Avoid making fermented corn, coconut, glutinous rice or potato products at home. Strict hygiene practices or procedures are required to reduce the risk of bongkrekic acid acid contamination.
Avoid consuming any food related to bongkrekic acid if you are unsure of its source or safety.
If white fungus or black fungus needs to be soaked, they should be refrigerated appropriately and avoid overnight soaking to minimize bacterial growth.
Good hygiene practices should be used when fermenting foods, such as disinfecting all food contact surfaces to prevent undesirable contamination of food by bacteria.
When handling food at home, be sure to handle raw and cooked food separately to avoid the risk of cross-infection.
If the food is expired or spoiled, it must be discarded directly.
The Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare, Food and Drug Administration reminds the public that if anyone has suspected symptoms of poisoning after eating similar meals at the above-mentioned stores recently, they should seek medical treatment as soon as possible and keep food samples to facilitate correct diagnosis and treatment.
Source:
Bongkrekic Acid: Safety of Fermented Corn and Coconut Products
Bongkrekic Acid—a Review of a Lesser-Known Mitochondrial Toxin
Epidemiology of foodborne bongkrekic acid poisoning outbreaks in China, 2010 to 2020
Further reading: